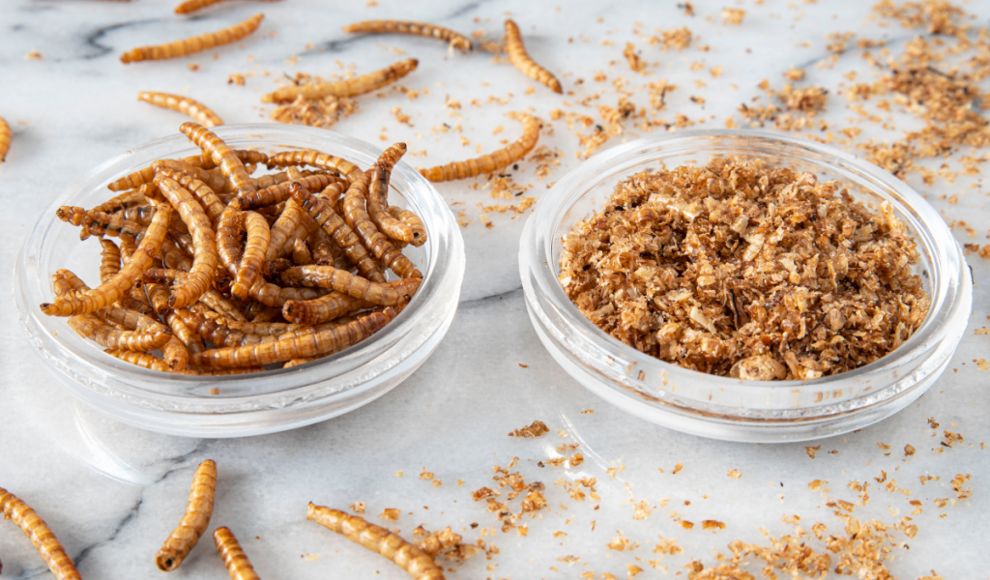
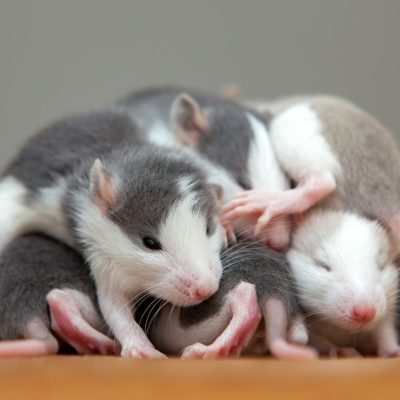
Insects and other foods containing chitin, a widely distributed biomolecule found in the exoskeletons of insects and shells of crustaceans, have been found to trigger an immune response that affects digestion and could aid in weight loss. Researchers at the Washington University School of Medicine have discovered that chitin activates the immune system, causing stomach cells to increase the production of enzymes necessary for digestion. The study found that mice that were unable to produce chitinase, the enzyme needed to break down chitin, gained less weight and had lower body fat levels than those that could produce the enzyme. The researchers are now investigating whether the same effects could be seen in humans and whether chitin could be added to human diets to help control obesity.
According to the study published in the journal Science, the immune system is involved in the digestion of chitin. Foods containing chitin cause an immune response that stimulates stomach cells to increase the production of chitinase enzymes, which are necessary for digestion. The researchers found that mice that were unable to produce chitinase gained less weight and had lower body fat levels than those that could produce the enzyme. The researchers also found that chitin caused changes in the bacterial composition of the lower gastrointestinal tract in mice with gut bacteria, suggesting that gut bacteria also adapt to chitin-containing foods.
The researchers believe that the effects of chitin on metabolism could have a real metabolic benefit and are investigating ways to inhibit stomach chitinase enzymes. They are also exploring whether chitin could be added to human diets to help control obesity. The study provides new insights into the role of the immune system in digestion and could lead to new treatments for obesity and other metabolic disorders.