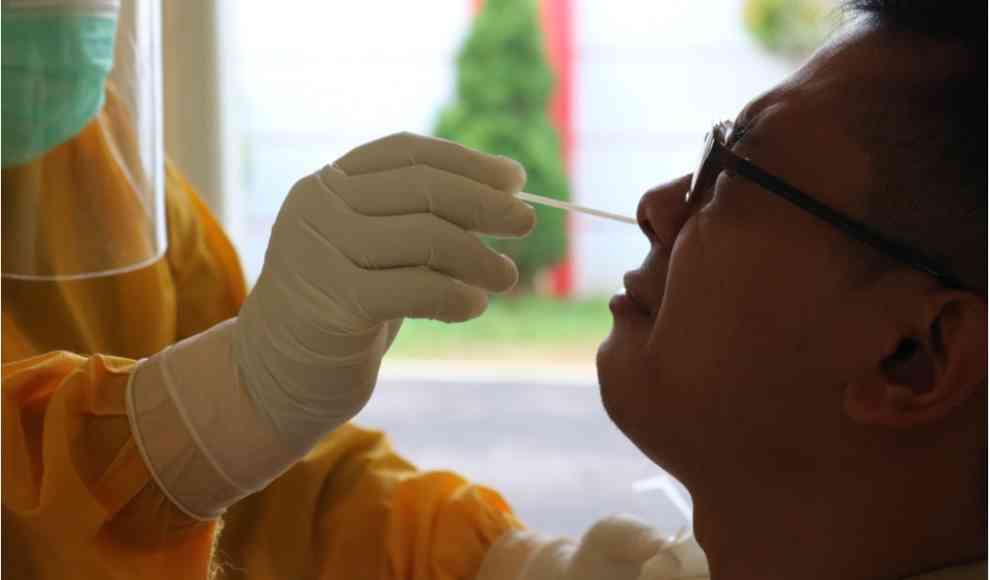
A recent study conducted by scientists at the Charité Universitätsmedizin in Berlin has investigated whether self-administered nasal swabs can provide accurate results for COVID-19 antigen tests. Currently, in Germany, only trained professionals are allowed to take the nasal-pharyngeal swabs required for antigen testing. However, self-administered tests could be useful in places like schools and nursing homes where many people gather in close proximity. The study found that self-administered nasal swabs were comparable in accuracy to professional nasal-pharyngeal swabs, with a sensitivity of 74.4% and 79.5%, respectively.
The study involved 289 participants with suspected COVID-19 symptoms who self-administered nasal swabs before a trained professional took a nasal-pharyngeal swab. The results of the antigen tests were compared to PCR tests, which are considered the gold standard for COVID-19 testing. The study found that the sensitivity of self-administered nasal swabs was comparable to that of professional nasal-pharyngeal swabs, with both methods having a sensitivity of nearly 96% for participants with a high viral load.
While the study’s results are promising, the researchers caution against relying solely on self-administered tests. They note that incorrect administration or interpretation of results could lead to false security. Further studies are needed to determine whether self-administered tests can be performed accurately by untrained individuals.
Despite the potential benefits of self-administered tests, they are not yet officially recommended by the researchers. However, the study’s findings suggest that self-administered tests could be a useful tool in increasing testing rates and identifying COVID-19 infections.