Fracking, the process of extracting natural gas, has become a controversial issue in the United States. While it is an effective method, it also poses significant risks to the environment and public health. A recent study has revealed alarming results regarding air pollution in and around fracking sites. This has raised concerns among experts and the public alike.
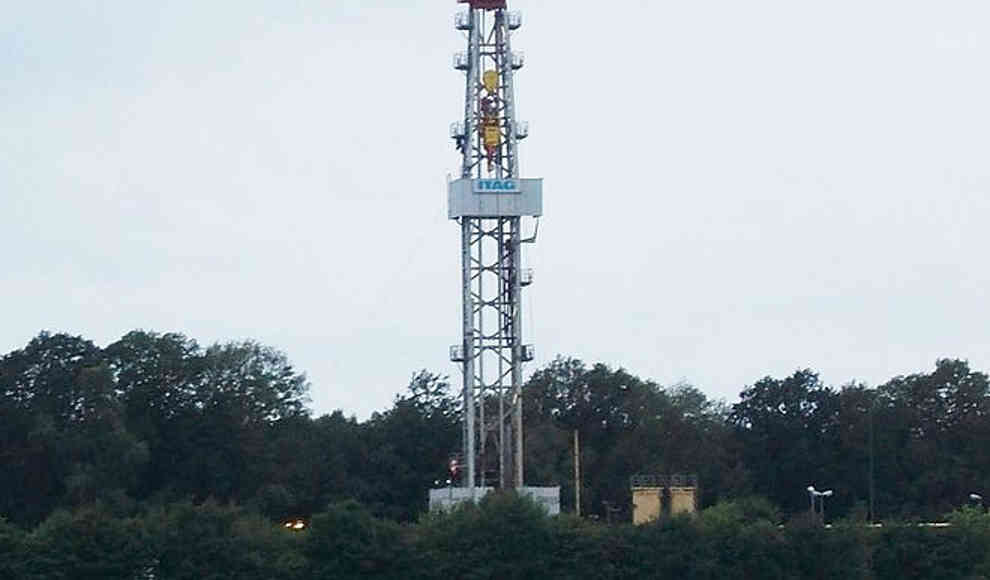
Fracking has become a booming industry in the US, replacing dwindling oil reserves. The process involves drilling up to 2,300 meters deep and injecting a mixture of water and chemicals to extract natural gas. This causes tiny earthquakes and releases volatile gases, which are then extracted through the drill pipes. While there have been numerous studies on the environmental and health impacts of fracking, a recent study has revealed that there are also immediate air pollution concerns associated with hydraulic fracturing.
David Carpenter, a professor at the University of Albany in New York, conducted a study in which air samples were taken from 11 locations in five states during fracking operations. The results showed significant increases in the concentration of various chemicals, including benzene, formaldehyde, and hydrogen sulfide. These chemicals are known to be carcinogenic and can cause a range of health problems, including dizziness, headaches, and nausea. The US Environmental Protection Agency and the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry have expressed alarm at these findings, citing the immediate and long-term health effects of exposure to these chemicals.
The study has raised concerns among the public and experts alike, highlighting the need for stricter regulations and greater transparency in the fracking industry. While fracking may be an effective method of extracting natural gas, it is clear that the risks associated with it cannot be ignored.