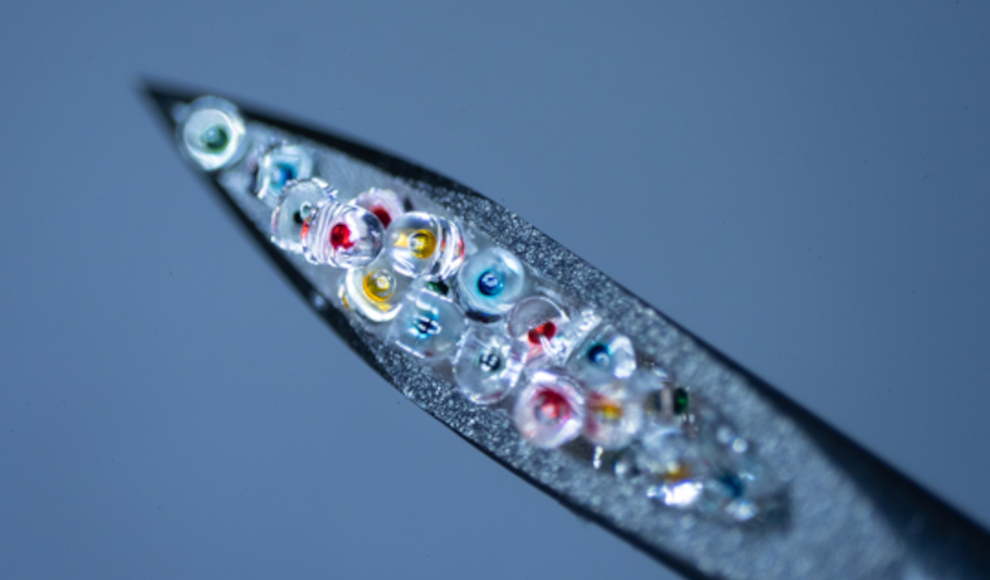
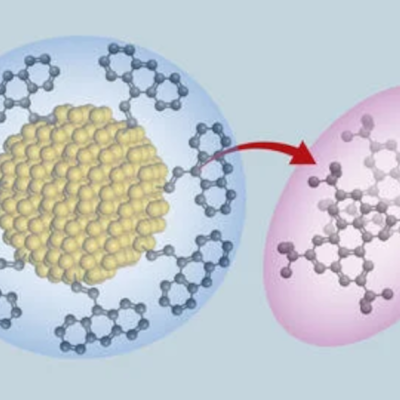
Researchers at Rice University have developed a solution to the problem of patients forgetting to take their medication during long-term therapies. They have created non-toxic, biodegradable capsules containing nanoparticles that release drugs at predetermined times in the body. The capsules can be administered directly into the bloodstream with a standard syringe. Doctors estimate that around half of long-term therapies are taken irregularly, leading to an estimated 100,000 deaths and healthcare costs of between $100bn and $300bn in the US alone. The Rice University team used lithography and 3D printing technology to produce the capsules, which are made from PLGA, a biologically compatible polymer. The capsules can contain different drugs and release them at different rates, with some lasting up to five weeks.
The researchers have named their system “Particles Uniformly Liquified and Sealed to Encapsulate Drugs” (PULSED). The capsules can be used for localised treatment, remaining in a specific area of the body where the drugs are released. This reduces side effects and makes chemotherapy more effective by concentrating the drugs in the tumour rather than the rest of the body. The capsules are not a new concept in medicine, but the Rice University team’s innovation lies in their use of non-toxic, biodegradable materials that can be injected into the bloodstream with a standard syringe. The capsules are expected to be particularly useful for long-term therapies, where patients often forget to take their medication regularly.
Kevin McHugh, one of the researchers, said that the team had focused on ensuring that the drugs were released evenly over time, rather than in a large dose on the first day. This is a common problem with other drug delivery systems, where the first dose can be toxic and later doses may not be effective. The Rice University team’s capsules can release drugs over a period of up to five weeks, making them ideal for long-term therapies. The team’s research has been published in the journal Advanced Materials.