Scientists at the University of California have presented a new propulsion system called the Pellet-Beam Drive, which could significantly accelerate space travel and aid in space exploration. Current spacecraft take over a week to reach the moon, seven months to reach Mars, and several decades to reach the interstellar medium. The Pellet-Beam Drive could transport large masses over long distances at high speeds, potentially reaching the heliopause in under five years, compared to the 35 years it took the US Voyager 1 spacecraft. The concept has been selected as one of 14 in the NASA Innovative and Advanced Concepts program, receiving $175,000 for further development.
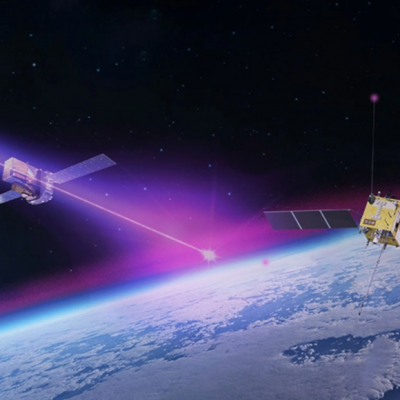
The Pellet-Beam Drive is a propulsion system that uses a particle beam to accelerate a spacecraft. The system requires two spacecraft, one in Earth’s orbit and one that will reach the target destination. The spacecraft in Earth’s orbit will direct a particle beam of micro-pellets towards the interstellar spacecraft. A portion of the pellets will be transformed into plasma by a laser beam, which will then accelerate the remaining pellets. This will create a glowing chain of pellets that could reach speeds of up to 120 kilometers per second. The impulse generated by the chain will then accelerate the interstellar spacecraft, allowing it to travel at high speeds.
The Pellet-Beam Drive could potentially reach the outer planets in less than a year, 100 astronomical units in three years, and 500 astronomical units in 15 years. The system requires less energy than a laser propulsion system and can transport heavier payloads. The scientists plan to use the funding from NASA to conduct experiments and calculations to determine the feasibility of the system. The Pellet-Beam Drive is still in the conceptual stage, but the researchers hope that it will enable faster space travel in the future.