Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry have created a new superconductor made of nickelate that loses its electrical resistance at minus 258.6 degrees Celsius. The team is now working on experiments to create a high-temperature superconductor that can conduct electricity without resistance at room temperature. Previously known superconductors, such as graphene, metal hydrides, sulfur hydride, and cuprates, can only conduct electricity without resistance near absolute zero. The discovery of a material that can be used as a superconductor at normal room temperature and pressure has yet to be found.
The search for superconductors has been challenging because scientists have not been able to determine when a material becomes superconducting. Researchers are looking for elements in the periodic table whose compounds could form superconductors. Scientists at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, affiliated with Stanford University, have focused on nickel in their search for new superconductors. Nickel is located next to copper in the periodic table, and nickel oxides have a crystal structure similar to cuprates, which have been shown to produce superconductors. The team believes that nickelates, or nickel oxides, could potentially create high-temperature superconductors.
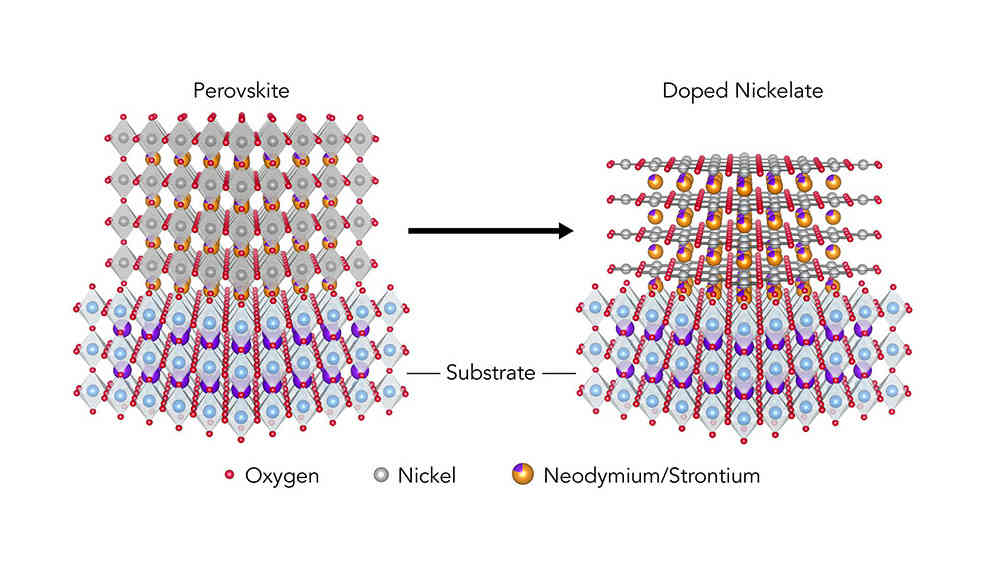
The production of a superconductor made of nickel oxides has been challenging because it has not been possible to create the necessary structure. The scientists used a neodymium-containing nickel oxide to form ultra-thin crystals on a strontium-titanium oxide plate. They then converted this structure into a strontium-containing nickelate in a multi-step process, resulting in a crystal structure that can be used to create superconductors. The team found that the strontium-doped nickelate becomes superconducting at minus 258.6 degrees Celsius. While the properties of the two superconductors differ in some ways, such as the fact that nickelates are not magnetic, the team hopes to continue their work to create a form of nickel oxide that can be used as a high-temperature superconductor.