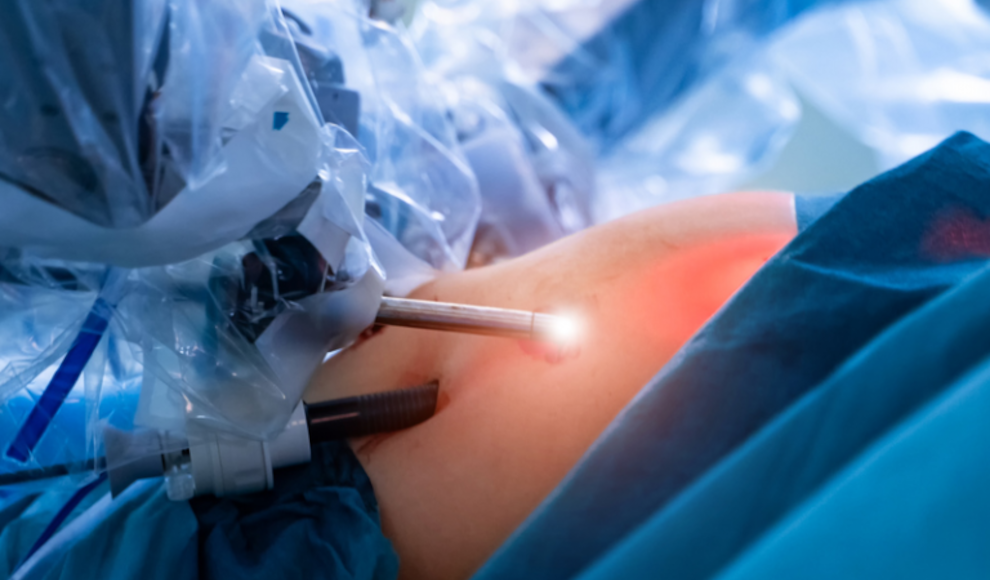
Robots are increasingly being used in the medical field to perform surgeries. A recent study compared the results of bladder removal surgeries performed by robots versus human surgeons. According to the study published in the JAMA medical journal by scientists from the University College London and the University of Sheffield, robots have great potential in surgical procedures. The study found that robotic surgery reduces the risk of needing another surgery by 52% compared to manual bladder removal by a doctor. Additionally, there were significantly fewer blood clots (77%) and postoperative recovery was “dramatically faster” with robotic surgery.
The study analyzed the weeks immediately following the surgery, and further studies have shown that the healing rate of cancer and long-term recovery are identical between robotic surgeons and human doctors. As a result of these positive findings, the scientists have recommended that the National Institute of Clinical Excellence (Nice) declare robotic surgery as the gold standard for larger abdominal surgeries. They believe that the significantly faster recovery time is evidence that robotic surgeons can improve the quality of life for patients.
The use of robots in medicine is becoming more common, with robots now able to autonomously maneuver catheters to the heart, remove brain tumors, and perform other complex surgeries. Recently, scientists from the University of Hong Kong even developed a flexible slime robot that can be used inside the human body. The potential benefits of robotic surgery are clear, and this study provides further evidence of its effectiveness.