Science Shop
Advertisement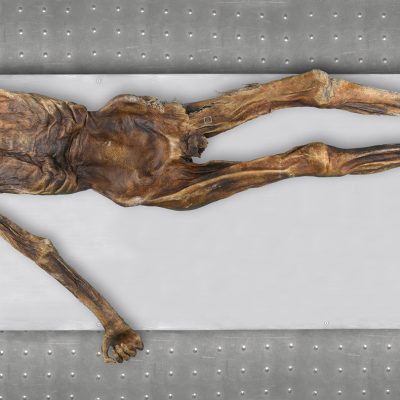
Ötzi’s DNA: Origin, Skin, Hair
- By Geert Devenster
- . December 9, 2023
A new study by the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig and the Institute for Mummies and the Iceman of Eurac Research in
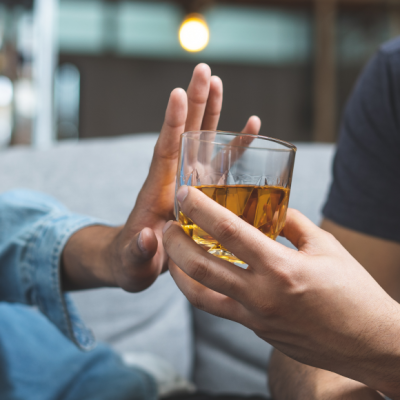

Alcohol Increases Risk of 60+ Diseases
- By Rolf Lewis
- . December 7, 2023
Alcohol Increases Risk of 61 Diseases, Including Previously Unrecognized Ones A study conducted on over 500,000 Chinese individuals has revealed that alcohol consumption increases the
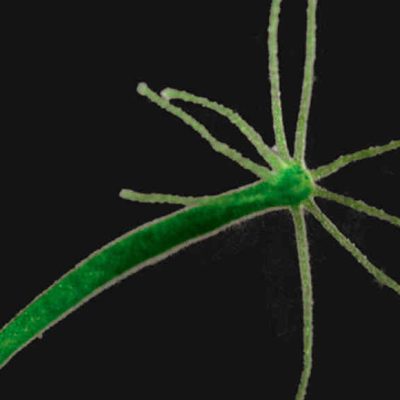

Chasing Immortality
- By Rolf Lewis
- . December 3, 2023
German scientists have discovered the gene for immortality in a freshwater polyp called Hydra, which is also present in humans. The researchers from the Christian-Albrechts-Universität
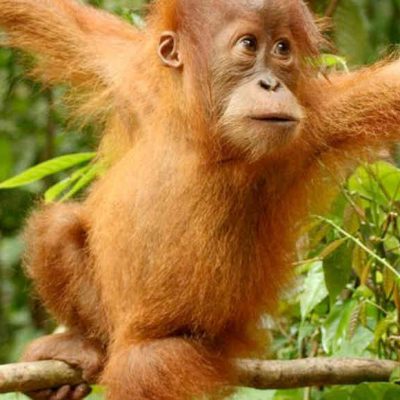

Ape Midlife Crisis
- By Rolf Lewis
- . December 3, 2023
A new study has found that chimpanzees and orangutans experience a midlife crisis, just like humans. Researchers from around the world studied over 500 primates
Gene Therapy Rejuvenates Mice
- By Rolf Lewis
- . November 30, 2023
A biotech company has successfully rejuvenated mice through gene therapy, and now aims to extend human life. Rejuvente Bio, based in San Diego, claims to

Do E-cigarettes lead to smoking?
- By Rolf Lewis
- . November 20, 2023
A recent study conducted by researchers at Queen Mary University of London (QMUL) has shed new light on the debate surrounding e-cigarettes and their potential

Income Boosts Self-Esteem
- By Geert Devenster
- . November 10, 2023
A higher income can improve one’s perceived self-worth, according to various studies. Researchers from the City, University of London found that comparing salaries with colleagues
Microplastics found in human heart
- By Rolf Lewis
- . November 9, 2023
A recent study conducted by the Capital Medical University (CMU) has found that microplastic particles can accumulate in the human heart and bloodstream. The study,

Do Humans Have Free Will?
- By Geert Devenster
- . October 28, 2023
The Libet experiments from the 1970s and 1980s suggested that humans do not have free will. Now, the experiments have been repeated to solve the

Discovery of Human Memory Variations
- By Rolf Lewis
- . October 19, 2023
New Study Reveals Reasons for Differences in Memory Performance The memory performance of different individuals varies significantly, and researchers have now discovered the reasons behind









